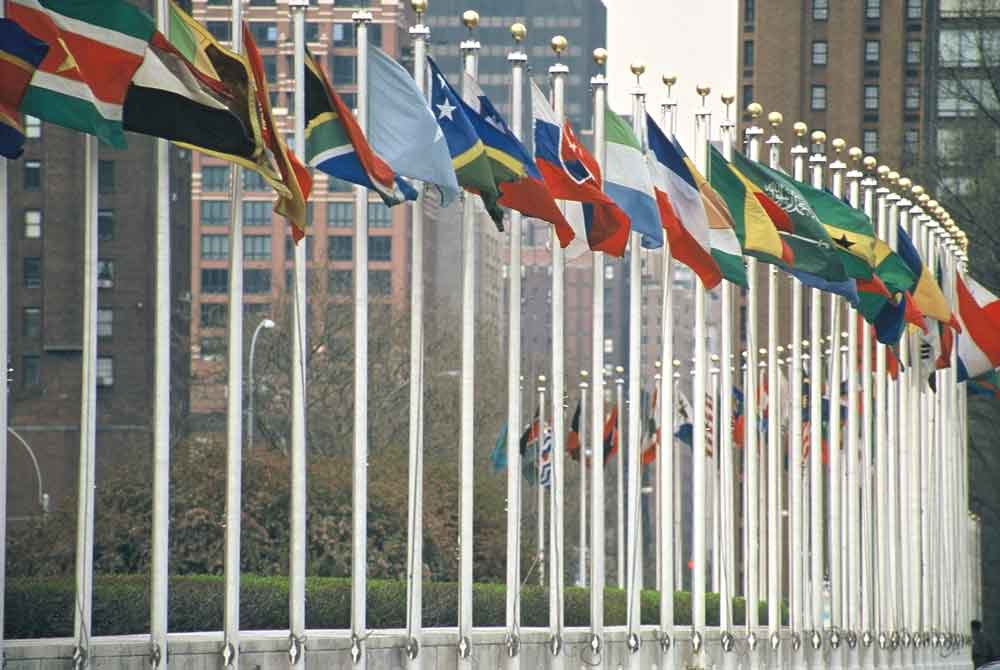
National flags stand as powerful symbols, representing the unique identity, heritage, and values of each country. These vibrant pieces of cloth are not just decorative items; they embody the spirit, history, and aspirations of a nation. For example, the stars and stripes of the American flag reflect its history of independence and unity, while the red, white, and blue of the French flag symbolize liberty, equality, and fraternity. Each element and color in a flag carries a story, whether it’s the green and gold of Brazil, symbolizing its lush forests and wealth, or the intricate design of the Mexican flag, featuring an eagle and serpent, which harks back to ancient Aztec legend.
These symbols are revered and respected, often evoking a sense of patriotism and pride among citizens. Flags fly high during national holidays, at international sporting events, and at times of mourning, serving as a reminder of the shared identity and collective memory of the people. Thus, national flags are more than mere banners; they are the fabric of national consciousness and pride.
Significance of National Flags
National flags serve as powerful symbols that represent the identity and unity of a nation. These vibrant pieces of fabric embody the history, culture, and values of the countries they represent. A flag can stir emotions of pride and patriotism, creating a sense of belonging among citizens. Each design, color, and symbol on a national flag holds profound meaning, often rooted in historical events, significant achievements, or cultural heritage. For instance, the stars on the American flag symbolize the states, while the stripes represent the original thirteen colonies.
Similarly, the Canadian flag features a red maple leaf, reflecting the country’s rich natural resources and commitment to unity and diversity. Flags are not just decorative; they are flown during national holidays, displayed in government buildings, and waved during international events to signify national presence and identity. The respect and honor given to a national flag are seen in how it is handled and displayed, often governed by strict protocols to maintain its dignity. Understanding and appreciating these symbols can foster a deeper connection to a country’s history and values.
Educational Value of Alphabetical Order Flags
Learning about national flags in alphabetical order can be an engaging and systematic approach to understanding the diverse symbols of the world. This methodical arrangement helps learners grasp the wide variety of flags without feeling overwhelmed. By studying flags in alphabetical order, one can easily remember and identify each nation’s emblem. For instance, starting with Afghanistan’s tricolor flag and moving on to Zimbabwe’s unique bird symbol provides a structured path to knowledge. This educational technique is particularly effective for young students or beginners who may find the random assortment of flags confusing.
Alphabetical learning also aids in the organization of information, making it easier to locate and reference specific flags. It encourages a step-by-step exploration of the globe, fostering curiosity and a global perspective. Additionally, this method can be turned into interactive activities such as quizzes or flag-matching games, making the learning process fun and engaging. By the end of such a journey, learners not only recognize the flags but also understand the stories and significance behind them, enriching their global awareness.
Learning Through Alphabetical Order
Understanding flags through alphabetical order can be an excellent educational tool. Arranging flags alphabetically makes it easier for learners to systematically study and memorize the diverse symbols of the world. This methodical approach ensures that no nation is overlooked and provides an organized way to absorb information. For instance, starting with Afghanistan’s flag, which features a mosque at its center, learners can progress to Zimbabwe’s flag, with its unique bird symbol.
This structure can help students draw connections between countries with similar colors or designs, fostering a deeper understanding of global cultures. Additionally, alphabetical sorting can aid in comparing and contrasting the flags of neighboring countries or those with historical ties, highlighting both similarities and differences. This method transforms the learning process into a more engaging and manageable experience, making the vast array of world flags accessible and memorable for all ages.
Cultural Significance Embedded in Flags
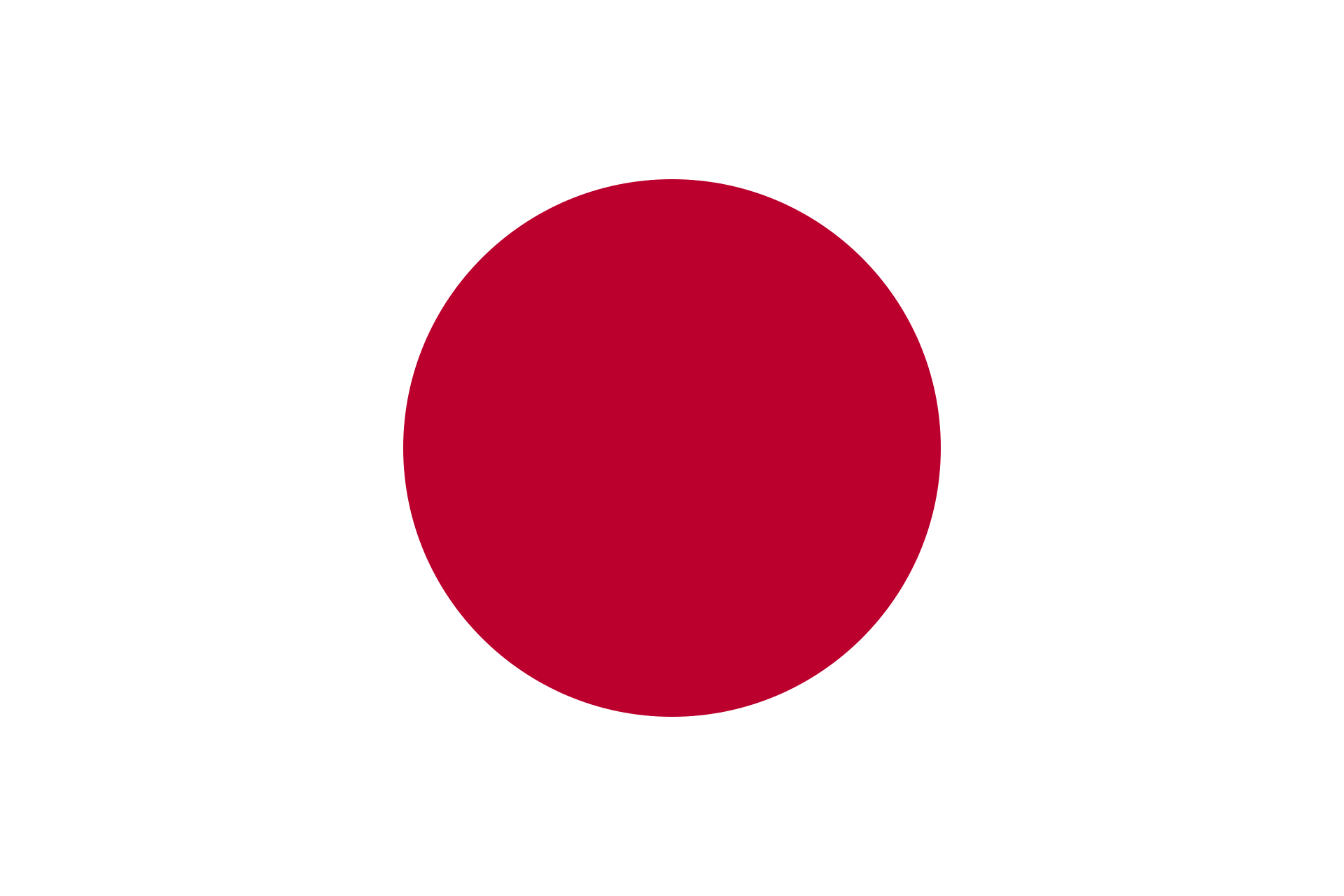
Every national flag tells a story, woven into its colors and symbols, reflecting the cultural essence and historical milestones of a nation. For example, the Japanese flag, with its simple red circle on a white background, symbolizes the rising sun and the country’s identity as the “Land of the Rising Sun.” Similarly, the Brazilian flag’s green and yellow hues represent the lush forests and wealth of resources, respectively. These cultural symbols are not arbitrary; they are carefully chosen to convey a nation’s heritage, values, and aspirations.
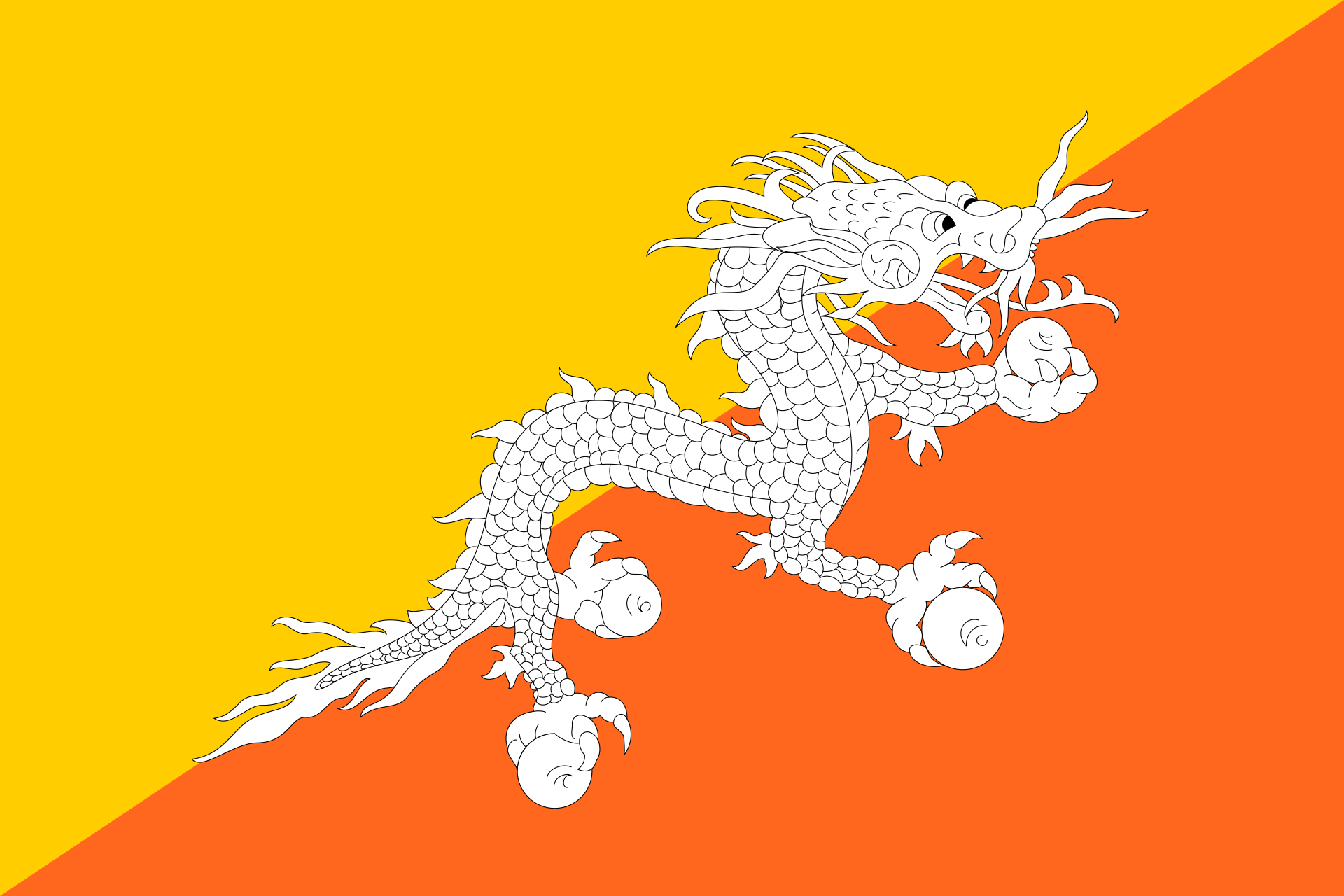
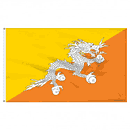
The dragon on Bhutan’s flag signifies the country’s name in its local language, Druk Yul, or “Land of the Thunder Dragon,” illustrating a deep connection to its mythology and national identity. By delving into the meanings behind these flags, one gains insight into the unique characteristics and pride of each nation. This cultural exploration fosters a deeper appreciation and respect for global diversity, highlighting the importance of each country’s contributions to the world tapestry. Understanding the cultural significance embedded in national flags enriches our global perspective and appreciation for international traditions and histories.
The Educational Value of Flags
Studying flags offers significant educational benefits, extending beyond simple recognition. It opens a window into the geography, politics, history, and culture of different nations. Each flag’s design elements are often deeply intertwined with the country’s identity and historical milestones. For example, the Union Jack in the flag of the United Kingdom reflects the unification of its constituent countries, while the rising sun on Japan’s flag symbolizes a new dawn and the country’s nickname, “The Land of the Rising Sun.”
By learning about these flags, students gain insights into the stories and symbols that shape national narratives. Teachers can use flags as a starting point for discussions on international relations, colonial histories, and cultural diversity, making the subject matter more dynamic and engaging. Moreover, this study encourages a sense of global awareness and respect for other cultures, fostering an appreciation for the diverse tapestry of human society.
Symbolism and Design Elements in Flags
The design elements of national flags are meticulously chosen to represent various aspects of a nation’s identity, values, and aspirations. Colors, shapes, and symbols are not mere decorations but are imbued with deep meanings. For instance, the horizontal stripes of the German flag stand for unity, justice, and freedom—core principles of the nation. The crescent and star on the Turkish flag symbolize the country’s Islamic heritage and its connection to ancient civilizations. These design elements often convey messages of resilience, hope, and unity, serving as reminders of a nation’s journey and struggles.
The intricate patterns and vibrant colors of the Indian flag, with its spinning wheel at the center, reflect the country’s rich history, cultural diversity, and struggle for independence. By examining these design elements, one can uncover layers of historical and cultural narratives that shape a nation’s identity. This symbolism in flags offers a visual language that communicates powerful stories and ideals, fostering a sense of national pride and unity among citizens. It also provides a means for individuals to connect with their heritage and understand their place within the broader national context.
Importance of Respecting National Flags
Respecting national flags is crucial as it reflects the honor and dignity of the nation it represents. Flags are treated with great reverence, following specific protocols to ensure they are displayed and handled properly. For instance, the flag should never touch the ground or be used for inappropriate purposes, as such actions are seen as disrespectful. The proper folding, raising, and lowering of the flag are rituals that symbolize respect and commitment to the nation’s values. During national holidays and significant events, flags are prominently displayed to remind citizens of their shared identity and collective heritage.
Disrespecting a flag can lead to significant consequences, as it is seen as an insult to the nation and its people. This respect extends beyond national borders; international events often see a display of multiple flags, symbolizing unity and mutual respect among nations. By understanding and adhering to the protocols associated with national flags, individuals show their respect for the country’s history, achievements, and values, fostering a sense of national pride and unity. This reverence underscores the importance of national symbols in maintaining a nation’s dignity and identity on the global stage.
Flags as Tools for Global Education
National flags serve as excellent tools for global education, providing insights into the diverse cultures and histories of the world. Through the study of flags, learners can explore geographical locations, historical events, and cultural practices. Flags like those of Nepal, with its unique non-rectangular shape, and Switzerland, with its square design, teach about the uniqueness and diversity of national symbols. These differences spark curiosity and encourage deeper exploration into why each flag is designed in a particular way. Educational programs that incorporate the study of national flags help students develop a global perspective, fostering an understanding and appreciation of international diversity.
This knowledge can be enhanced through activities such as creating flag-themed art projects, writing essays on the history of specific flags, or participating in flag quizzes. By integrating flags into the curriculum, educators can make learning about the world engaging and interactive. This approach not only enriches students’ knowledge but also promotes respect and empathy for different cultures, preparing them to be informed and responsible global citizens.
Promoting Unity Through Flags
National flags play a significant role in promoting unity and solidarity among citizens. They are often displayed during national celebrations, sports events, and international gatherings, symbolizing collective identity and pride. When a country’s flag is raised at events such as the Olympics, it fosters a sense of unity and pride among the spectators and participants from that nation. The flag becomes a rallying point, bringing people together regardless of their differences.
It embodies the shared values, history, and aspirations of a nation, serving as a reminder of what unites its people. In times of crisis, such as natural disasters or national emergencies, the sight of the national flag can provide a sense of hope and solidarity, reinforcing the idea that the nation stands together. This unifying power of flags helps strengthen national identity and cohesion, encouraging citizens to work together towards common goals. The flag’s role in promoting unity underscores its importance as a national symbol, fostering a sense of belonging and mutual support among the nation’s people.
Engaging Activities for Learning Flags
Incorporating interactive activities enhances the learning experience when studying flags. Games, quizzes, and creative projects can make the process fun and memorable. For instance, a classroom activity could involve matching flags with their respective countries or a drawing contest where students replicate and color different national flags. Digital tools like apps and online games can also provide interactive ways to test knowledge and track progress. Motivation – Mind – Success – Thinking – Productivity – Happiness
Creating a “Flag of the Day” segment, where students present interesting facts about a selected flag, can stimulate curiosity and encourage independent research. These activities not only solidify knowledge but also build teamwork and presentation skills. By transforming the learning process into an engaging and interactive journey, students are more likely to retain information and develop a lasting interest in global studies.
The Global Connection
Exploring flags fosters a sense of global interconnectedness and mutual respect. It reminds us that despite geographical distances and cultural differences, there are universal themes and shared histories that connect us. The colors red, white, and blue, for example, appear in the flags of numerous countries, symbolizing bravery, peace, and freedom respectively. This shared symbolism can be a starting point for discussions about common values and aspirations.
Furthermore, understanding the significance of each flag promotes empathy and appreciation for the struggles and triumphs of other nations. As students delve into the stories behind each flag, they gain a greater understanding of the world and the diverse experiences that shape it. This global perspective is crucial in an increasingly interconnected world, fostering a mindset of cooperation and mutual respect.